In the modern era, where environmental concerns are at the forefront of global consciousness, it’s imperative for industries to adapt to eco-conscious practices. In Indonesia, a country renowned for its vibrant industrial landscape, the concept of sustainable factory development is gaining significant traction. The transformation towards eco-conscious industrialization is not only a necessity but also a tremendous opportunity to create a more sustainable future for the nation. In this article, we delve into the strategies and benefits of building sustainable factories in Indonesia’s industrial parks.
The Urgency of Eco-Conscious Industrialization

Indonesia’s rapid industrialization over the past few decades has been accompanied by environmental challenges. As the nation continues to grow economically, there is a pressing need to minimize the adverse environmental impact of industrial activities. Eco-conscious industrialization seeks to strike a balance between economic development and environmental preservation.
Sustainable Factory Design
One of the fundamental aspects of eco-conscious industrialization is the design of sustainable factories. These factories are built with a focus on minimizing energy consumption, reducing waste, and incorporating green technologies. By using energy-efficient lighting, solar panels, and advanced insulation techniques, sustainable factories significantly lower their carbon footprint.
Efficient Resource Management
Resource management is critical for eco-conscious industrialization. Sustainable factories in Indonesia are embracing techniques like water recycling and waste-to-energy conversion to make the most of available resources while reducing their environmental impact. Efficient resource management not only benefits the environment but also contributes to cost savings.
Eco-Friendly Materials
The choice of construction materials plays a vital role in building eco-conscious factories. Sustainable factories prioritize the use of eco-friendly materials such as recycled steel, low-VOC paints, and sustainable wood products. This not only reduces the environmental impact of construction but also ensures that the factory operates in an eco-conscious manner.
Indonesia’s Eco-Friendly Industrial Parks

Indonesia boasts numerous industrial parks that are now taking a proactive approach to promoting eco-conscious industrialization. These industrial parks are strategically located, well-equipped, and designed to facilitate sustainable practices among the factories operating within them.
Infrastructure Support
Industrial parks in Indonesia offer state-of-the-art infrastructure that aligns with eco-conscious objectives. This includes reliable energy sources, efficient waste management systems, and access to public transportation. Such infrastructure minimizes the need for individual factories to invest in their own eco-friendly systems, making eco-conscious industrialization more cost-effective.
Regulatory Incentives
The Indonesian government is actively encouraging sustainable practices within industrial parks. This includes offering incentives to factories that adopt eco-friendly technologies and processes. These incentives may include tax breaks, grants, or preferential treatment in government contracts, which make sustainable industrialization an attractive option for businesses.
Collaborative Ecosystem
Industrial parks foster a collaborative ecosystem where factories can share best practices and innovations related to eco-conscious industrialization. This knowledge-sharing approach accelerates the adoption of sustainable practices, benefitting all stakeholders within the industrial park.
Economic and Environmental Benefits
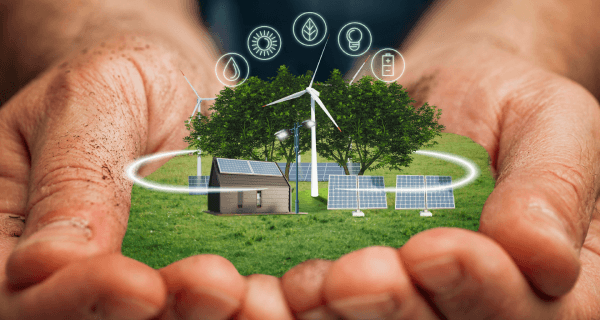
Embracing eco-conscious industrialization in Indonesia’s industrial parks yields a range of benefits, both economic and environmental.
Cost Savings
Sustainable factories often experience significant cost savings in the long run. Reduced energy consumption, efficient resource management, and the use of eco-friendly materials translate into lower operational costs. This allows businesses to remain competitive while minimizing their environmental impact.
Enhanced Reputation
Eco-conscious industrialization also enhances a company’s reputation. Consumers and investors are increasingly favoring businesses that prioritize sustainability. A positive environmental track record can attract customers, investors, and partners who share the same eco-conscious values.
Reduced Environmental Footprint
The most apparent benefit of eco-conscious industrialization is the reduction of the environmental footprint. Sustainable factories emit fewer greenhouse gases, produce less waste, and use fewer natural resources. This contributes to cleaner air, water, and a healthier ecosystem for all.
Long-Term Sustainability
By adopting eco-conscious practices, industries in Indonesia contribute to the long-term sustainability of the nation’s industrial landscape. This ensures that future generations can enjoy the benefits of industrialization without compromising the environment.
Overcoming Challenges of Eco-Conscious Industrialization

Transitioning to eco-conscious industrialization is not without its challenges. Here are some common hurdles that industries face:
Initial Investment Costs
Implementing eco-conscious technologies and practices often requires substantial upfront investments. Companies may be hesitant due to concerns about the immediate financial impact.
Resistance to Change
Change can be met with resistance, especially in well-established industries. Employees and management may be hesitant to adopt new practices or technologies.
Solutions and Strategies for Overcoming Obstacles

Successful eco-conscious industrialization requires creative solutions to these challenges:
Financial Incentives
Government incentives, as discussed earlier, can help offset the initial costs of eco-conscious practices. This can include tax breaks, grants, or subsidies.
Employee Training and Engagement
Providing comprehensive training and engaging employees in the transition process can mitigate resistance. When employees understand the benefits and their role in eco-conscious practices, they are more likely to embrace change.
Conclusion
Environmentally conscious industrialisation is more than a trend; it is required for the long-term growth of Indonesia’s industrial sectors. Businesses may lead the road to a better future by building sustainable factories, implementing efficient resource management, and using environmentally friendly products.
Subang Smartpolitan’s industrial area provides the ideal environment for this change, with supporting infrastructure and a collaborative ecosystem. Designed as a smart, green and sustainable township, Subang Smartpolitan will have huge economic and environmental benefits, making it a win-win situation for both companies and the planet.
Let us acknowledge that environmentally aware industrialization is the way to a more sustainable and prosperous future for Indonesia and the world as we move forward. It is time for industry to band together and build a brighter and more environmentally friendly future in Indonesia’s industrial areas.

