Lean manufacturing principles are transformative strategies that can revolutionize how businesses operate, leading to improved efficiency, reduced waste, and enhanced customer satisfaction. At the core of lean manufacturing is the idea of maximizing value for customers while minimizing unnecessary activities and costs. Whether you’re a seasoned industry professional or new to the world of manufacturing, understanding and applying these principles can significantly impact your operations.
This article will guide you through the five core principles of lean manufacturing and how they can be strategically applied to not only manufacturing settings but also beyond, into various sectors like healthcare and software development. We’ll also delve into the opportunities that specific industrial areas like Suryacipta and Subang Smartpolitan offer to businesses aiming to adopt lean practices.
Let’s embark on this journey to discover how lean manufacturing can transform your business and prepare it for future challenges and opportunities.
What are Lean Manufacturing Principles?
Lean manufacturing principles are a set of methodologies aimed at creating more value for customers with fewer resources. Originating from the Toyota Production System, these principles focus on eliminating waste within manufacturing systems, ensuring that every step of the production process adds value to the product or service and meets customer demands as efficiently as possible.
The essence of lean manufacturing lies in understanding what your customers value and continuously optimizing your processes to deliver that value most efficiently. This approach is not just about cutting costs or reducing time; it’s about creating a dynamic system that can adapt to changing customer needs and market conditions.
In today’s competitive business environment, the importance of lean principles cannot be overstated. Companies across the globe, regardless of their industry, size, or market, are turning to lean manufacturing to improve their operational efficiency, enhance product quality, and increase customer satisfaction. By adopting lean principles, businesses can streamline their operations, reduce waste, and foster a culture of continuous improvement, positioning themselves for long-term success and sustainability.
5 Core Principles of Lean Manufacturing
Transitioning into the heart of lean manufacturing, we encounter its five core principles, pivotal for transforming any production system into a lean, efficient powerhouse. These principles guide organizations to eliminate waste, enhance productivity, and ultimately deliver greater value to their customers. Let’s delve into the first of these principles: identifying value.
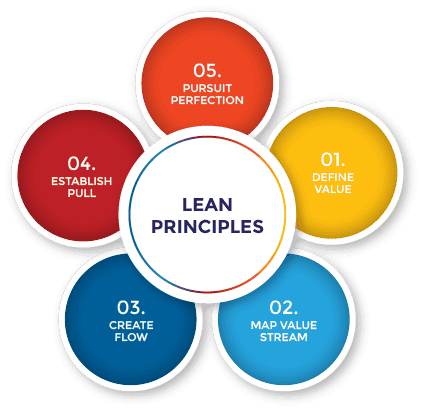
Principle #1: Define Value
At its core, the principle of identifying value is about understanding what your customer truly needs and values in your product or service. It’s the starting point of the lean journey, ensuring that every effort made and every resource spent contributes directly to creating something that the customer is willing to pay for. This principle challenges us to look through the eyes of our customers, understanding their needs, preferences, and the problems they seek to solve.
Definition and Significance of Value from the Customer’s Perspective
Value, from the customer’s perspective, is not just about the price tag; it’s about the utility, quality, and satisfaction a product or service provides. In lean manufacturing, identifying this value means stripping away assumptions and getting to the heart of what makes your offering essential to the customer. This understanding not only informs what you produce but also how you produce it, ensuring that each step in the manufacturing process adds real value.
Strategies for Identifying Value in Various Industries
Identifying value requires a tailored approach, as what constitutes value can vastly differ from one industry to another, and even from one customer segment to another within the same industry. Here are a few strategies to uncover this critical insight:
- Customer Interviews and Feedback: Directly engaging with your customers to gather insights about their needs and pain points.
- Market Research: Analyzing market trends, competitors, and industry benchmarks to understand where your product can offer unique value.
- Value Proposition Canvas: Utilizing tools like the Value Proposition Canvas can help in mapping out customer profiles and value propositions, making it clearer how your product or service meets the customer’s needs.
By putting the principle of identifying value at the forefront of your lean manufacturing efforts, you ensure that every process, every product, and every innovation is aligned with what your customers truly value. This not only streamlines your operations but also solidifies your position in the market by consistently meeting and exceeding customer expectations.
Principle #2: Map the Value Stream
Diving deeper into lean manufacturing, the second principle, mapping the value stream, is where you start visualizing the journey of your product from raw material to customer delivery. Value Stream Mapping (VSM) is a vital tool in this process, allowing you to see every step of your production and identify where value is added and where waste occurs.
Explanation of Value Stream Mapping and Its Importance
Value Stream Mapping is essentially a diagram that displays all the steps involved in delivering your product or service. It highlights the flow of materials and information as a product makes its way through the value chain. The importance of VSM lies in its ability to provide a holistic view of the production process, pinpointing inefficiencies, redundancies, and bottlenecks that could be slowing you down or adding unnecessary costs.
Step-by-Step Guide to Mapping the Value Stream in Manufacturing
- Identify the Product or Product Family: Choose a product or a family of products that go through similar processing steps.
- Map the Current State: Document all the steps in the current process, including wait times, inventories, and movements, to create a baseline for improvement.
- Identify and Categorize Waste: Look for the seven wastes of lean (defects, overproduction, waiting, non-utilized talent, transportation, inventory, and extra processing) within your value stream.
- Design the Future State: Envision a leaner process by eliminating identified wastes and optimizing the remaining steps.
- Implement and Test Changes: Start small, implementing changes that move you toward your future state vision, and measure the impact.
- Continuous Improvement: Value stream mapping is not a one-time activity. Regular reviews and updates to the map are essential as improvements are made and conditions change.
Principle #3: Create Flow
Once the value stream has been mapped, the next step is to ensure that your production processes flow as smoothly as possible. Creating flow is about making sure that work progresses through manufacturing with minimal stops and starts, ensuring that value is delivered to customers efficiently.
Techniques to Ensure Smooth Flow of Production Processes
- Work Cell Design: Organizing workstations and equipment to minimize movement and handling, creating a more efficient production line.
- Pull Systems: Implementing pull systems like Kanban to control the flow of materials based on customer demand, rather than pushing products through production based on forecasts.
- Load Leveling: Balancing the production load to smooth out spikes and dips in demand, helping to maintain a steady flow.
- Cross-Training Employees: Developing a flexible workforce that can adapt to changing needs and fill in wherever needed to maintain flow.
Case Studies on Overcoming Common Obstacles to Flow
Several organizations have successfully overcome flow obstacles by applying lean techniques. For instance, a car manufacturer reorganized their assembly line into work cells, significantly reducing the distance parts traveled and improving production time. Another example is a hospital that implemented pull systems for medical supplies, drastically cutting down on waste and wait times for patients.
Creating a smooth flow in production processes not only enhances efficiency but also improves quality and responsiveness to customer demands, driving greater satisfaction and loyalty.
Principle #4: Establish Pull
Moving forward in our exploration of lean manufacturing principles, we arrive at the fourth cornerstone: establishing a pull system. This principle is about ensuring that production is directly tied to demand, a shift from the traditional push production model that can lead to overproduction and waste.
The Concept of Pull System vs. Traditional Push Production
In traditional push production systems, products are manufactured in anticipation of future demand, based on forecasts. This approach often results in excess inventory, wasted resources, and a disconnect between what’s produced and what customers actually want. In contrast, a pull system reverses this logic. Production is triggered by actual demand, ensuring that nothing is made without a specific request from the next step in the process, whether that’s a direct customer order or a signal from downstream operations.
Implementing a Pull System in Manufacturing and Service Sectors
Implementing a pull system requires a paradigm shift in how production and services are planned and executed. Here’s how you can begin this transformation:
- Understand Customer Demand: Start with a clear analysis of your demand patterns. Knowing the volume and frequency of customer orders is critical.
- Use Kanban Signals: Implement Kanban or similar visual signaling systems to indicate when more product needs to be produced or services rendered. These signals help synchronize production with actual demand.
- Limit Work in Progress (WIP): Set limits on the amount of unfinished work at any stage of production. This reduces lead times and inventory levels, making the system more responsive.
- Flexibility: Ensure your processes and workforce are flexible enough to adapt to changes in demand without significant delays or disruptions.
Examples from Both Sectors:
1. In the Manufacturing Sector
A company might set up a Kanban system where components are only reordered or produced when their quantities fall below a certain threshold, directly tied to the upcoming production schedules. This ensures materials are available just in time for assembly, reducing inventory costs and space requirements.
2. In the Service Sector
A restaurant could implement a pull system by preparing dishes based on real-time orders rather than predicting demand and preparing food in advance. This approach minimizes waste, ensures freshness, and improves customer satisfaction by delivering exactly what is ordered.
Establishing a pull system not only aligns production more closely with actual demand but also fosters a culture of agility and responsiveness. By focusing on what is needed, when it’s needed, businesses can dramatically reduce waste and improve efficiency, leading to higher quality products and services tailored to customer needs. This principle is crucial for organizations aiming to stay competitive in fast-paced markets where customer preferences and demand can change rapidly.
Principle #5: Pursuit Perfection
As we delve into the final principle of lean manufacturing, we embrace the concept of seeking perfection. It’s about fostering a culture of continuous improvement where the journey towards excellence is never-ending. This principle is the heartbeat of lean manufacturing, driving organizations to constantly challenge the status quo and seek ways to do things better, faster, and more efficiently.
Continuous Improvement as a Core Philosophy of Lean Manufacturing
The pursuit of perfection in lean manufacturing is not about achieving a flawless state but about continuously improving every process, product, and service. It’s an acknowledgment that there is always room for improvement, no matter how efficient a system may seem. This philosophy encourages a proactive approach to problem-solving, where every employee is empowered to identify and eliminate waste in their area of work.
Examples of Lean Tools and Practices That Drive Perfection
Several lean tools and practices are instrumental in guiding organizations on their path to perfection. Here are a few key examples:
- Kaizen: This Japanese term for “change for better” refers to activities that continuously improve all functions and involve all employees. Kaizen events or workshops are organized to focus on specific areas for improvement.
- 5S: A methodology that focuses on maintaining an organized and clean workplace to enhance productivity and safety. The 5S stands for Sort, Set in order, Shine, Standardize, and Sustain.
- PDCA Cycle (Plan-Do-Check-Act): A four-step management method used for the control and continuous improvement of processes and products. It’s a fundamental part of the lean manufacturing toolkit.
- Root Cause Analysis: A problem-solving method used to identify the underlying reasons for a problem, ensuring that solutions address the actual issue rather than its symptoms.
By embedding the principle of seeking perfection into the fabric of an organization, businesses can cultivate an environment where continuous improvement is the norm, not the exception. This relentless pursuit not only drives operational efficiency and reduces waste but also fosters innovation, employee engagement, and customer satisfaction. Through the strategic application of lean tools and practices, organizations can steadily progress toward their ideal state of lean perfection, always moving forward, and always improving.
Read More The 6 Leading Trends Revolutionizing Indonesia’s Manufacturing Sector
Applying Lean Principles Beyond Manufacturing
As we venture beyond the traditional boundaries of manufacturing, the versatility of lean principles shines brightly across various sectors. Lean thinking is not confined to the factory floor; its philosophy of maximizing value while minimizing waste holds transformative potential for industries far and wide. Here, we’ll explore how these principles are applied in non-manufacturing settings like healthcare and software development, illuminating the universal appeal of lean practices.
Insights into the Application of Lean Principles in Non-Manufacturing Settings
In environments as diverse as healthcare and software development, the core lean principle of delivering value to the customer remains unchanged. However, the interpretation of ‘value’ and the ‘customer’ can differ. In healthcare, for example, the ‘customer’ could be a patient, and ‘value’ might be high-quality, timely care. In software development, ‘value’ might mean delivering functional, user-friendly applications that meet or exceed customer expectations.
The application of lean in these sectors involves streamlining processes, reducing inefficiencies, and eliminating activities that do not add value from the customer’s perspective. This could mean reducing waiting times in hospitals or minimizing the number of steps to release a software update.
Overcoming Challenges in Lean Implementation
Embarking on a lean transformation journey can be as challenging as it is rewarding. While the benefits of implementing lean principles are vast, organizations often encounter several hurdles along the way. Recognizing these common challenges and understanding how to navigate them is crucial for a successful lean transformation. Let’s explore some of these obstacles and offer practical tips and solutions.
Common Challenges and Pitfalls in Adopting Lean Manufacturing Principles
- Resistance to Change: One of the most significant barriers to lean implementation is resistance from employees and management. Change can be daunting, and the shift to lean methodologies often requires a change in mindset and culture within the organization.
- Lack of Understanding: Without a clear understanding of lean principles and how they apply to the organization, it’s easy for initiatives to become misguided or lose momentum.
- Inadequate Leadership Support: Lean transformation requires strong leadership to drive change and support the team through the transition. Lack of leadership commitment can stall the implementation process.
- Focusing Only on Tools: While lean tools and techniques are valuable, focusing solely on these without understanding the underlying principles and philosophy can lead to superficial changes that don’t deliver long-term benefits.
Practical Tips and Solutions for Successful Lean Transformation
- Educate and Involve Everyone: Start by providing comprehensive training on lean principles for all employees and stakeholders. Involvement and education help demystify the process, build understanding, and reduce resistance.
- Cultivate a Lean Culture: Encourage a culture that views mistakes as opportunities for learning and improvement. Promoting an environment where every employee feels empowered to contribute ideas and suggestions is essential.
- Secure Leadership Commitment: Ensure that leaders at all levels are committed to the lean journey and are active participants in the transformation process. Leadership should consistently communicate the value of lean initiatives and celebrate progress and successes.
- Start Small and Scale: Begin with pilot projects or small areas within the organization to demonstrate the benefits of lean. Use the success of these initial efforts to build momentum and gradually expand lean practices across the organization.
- Focus on Continuous Improvement: Lean is not a one-time project but a continuous journey towards improvement. Foster a mindset of continuous learning and adaptability, regularly reviewing processes and outcomes to identify areas for improvement.
- Seek Feedback and Iterate: Regularly solicit feedback from employees and customers to gain insights into where processes can be optimized further. Be open to adapting your approach based on what you learn.
By anticipating these challenges and applying these practical tips, organizations can navigate the complexities of lean implementation more effectively. Remember, the journey towards lean is ongoing, and perseverance, adaptability, and a commitment to continuous improvement are key to achieving and sustaining success. Embracing lean principles not only enhances operational efficiency but also cultivates a culture of excellence and innovation.
Read More The Road to Sustainability: An In-depth Look at Electric Vehicle Production
Exploring the Advantages of Establishing Manufacturing Operations in Subang Smartpolitan

Subang Smartpolitan stands as a home for businesses looking to embrace lean manufacturing practices. Its meticulously designed infrastructure and supportive community environment provide the perfect foundation for companies aiming to streamline their operations and increase efficiency.
Subang Smartpolitan Support Lean Manufacturing Practices
Subang Smartpolitan offers state-of-the-art infrastructures designed to support lean manufacturing. From efficient logistics and transportation networks to reliable utilities, every aspect of the infrastructure supports the seamless flow of materials and information.
By establishing manufacturing facilities in Subang Smartpolitan, manufacturers gain a competitive edge, leveraging the industrial park’s robust infrastructure and community support to fully realize the benefits of lean manufacturing.
The Future of Manufacturing in Subang Smartpolitan

Subang Smartpolitan is set to revolutionize the industrial landscape, primarily by offering land tailored for manufacturing operations that are keen on embracing sustainability and lean practices. The infrastructure in Subang Smartpolitan is meticulously designed to support the seamless integration of innovative manufacturing technologies and lean methodologies. This forward-thinking approach ensures that manufacturing tenants can optimize their production lines, reduce waste, and significantly improve efficiency. By providing a robust foundation of smart utilities, logistics, and connectivity, Subang Smartpolitan is predicted to attract businesses that are at the forefront of the manufacturing sector’s evolution.
Moreover, the role of Subang Smartpolitan extends beyond merely selling industrial land; it aims to foster a community where sustainable and lean manufacturing flourishes. Through its commitment to environmental stewardship and operational excellence, Subang Smartpolitan is set to become a hub for companies that prioritize reducing their carbon footprint while enhancing productivity.
By encouraging the adoption of green technologies and lean principles, Subang Smartpolitan will not only shape the manufacturing tenants’ approach to production but also set new standards for sustainable development in the industry. This strategic focus promises a future where manufacturing operations are not just efficient and lean but also harmoniously integrated with the environment.
Read More Eco-Conscious Industrial Parks: Paving the Way to Sustainability


