Investment in Indonesia is your gateway to Southeast Asia’s future. While global financial instability weighs on markets, Indonesia continues to provide investor-friendly incentives, such as long-term tax holidays and infrastructure support. With a projected 5% growth rate, its diversified economy and growing digital landscape offer promising returns.
Discover why Indonesia is the right move for your next investment!
Why Is Indonesia’s Economy Still Resilient Despite Global Challenges?
Despite pressures from tightening global financial conditions and trade uncertainties, investment in Indonesia offers promising returns. The country maintains steady growth, supported by a projected GDP increase from 5.0% to 5.2% in 2025. Inflation remains manageable at around 2.8%, preserving consumer confidence and purchasing power. Also, efforts to attract foreign and domestic investment by creating a business-friendly environment and streamlining regulations contribute significantly to Indonesia’s economic stability and competitiveness.
What Are Indonesia’s Key Government Policies That Support Investment in Indonesia?

Indonesia is positioning itself as a top destination for foreign investment through bold legal and regulatory reforms. These changes simplify processes and create a more welcoming environment, making investing in Indonesia more appealing than ever before.
- Law No. 11 of 2020 on Job Creation (Omnibus Law)
The enactment of Law No. 11 of 2020 on Job Creation (Omnibus Law) marked a turning point for investment in Indonesia. By amending over 75 existing laws, this legislation streamlines licensing, land acquisition, and investment regulations across sectors. The law introduces a liberalized policy environment that permits 100% foreign ownership in many industries, replacing the outdated Negative List with a more progressive framework. - Presidential Regulation No. 49 of 2021
It replaced the previous Negative Investment List with the Positive Investment List, allowing over 200 business sectors to be fully open to foreign investment unless specifically restricted. The regulation permits 100% foreign ownership in most sectors, reducing restrictions and making Indonesia more attractive to foreign investors. This is a major shift from earlier policies that limited foreign ownership in many industries. The number of sectors closed or partially restricted to foreign investment has decreased by approximately 75% compared to the previous regulation. It introduces sector-specific foreign ownership caps, often allowing 70% for ASEAN investors and 67% for non-ASEAN investors, with the requirement that remaining shares be held by Indonesian shareholders, fostering local participation. - Investment Authority and Danantara
To further attract and manage foreign capital, Indonesia has established institutions like the Indonesia Investment Authority (INA) and Danantara. INA is designed to attract foreign co-investors to support domestic infrastructure projects and economic development. This approach helps leverage foreign capital to fund large-scale projects that might otherwise be difficult to finance solely through domestic resources. INA focuses on purchasing assets from state enterprises to improve their financial health, allowing them to undertake further development projects.
However, Danantara aims to optimize the value of Indonesia’s national assets, particularly state-owned enterprises (SOEs). By restructuring inefficient SOEs, Danantara can unlock new economic opportunities and improve the financial sustainability of these enterprises, making them more appealing to foreign investors. The establishment of Danantara is accompanied by government plans to introduce regulatory incentives, tax benefits, and streamlined processes. These measures are designed to create a more investor-friendly environment, further encouraging foreign investment in Indonesia.
Which Sectors Offer the Most Promising Opportunities for Investment in Indonesia?

1. Manufacturing
Indonesia’s competitive labor costs, strategic location, and abundant natural resources are transforming it into a global manufacturing hub. The automotive industry, particularly electric vehicle (EV) production, is seeing rapid growth. Backed by government incentives and the allowance of 100% foreign ownership, this sector is powered by Indonesia’s rich nickel reserves, a critical resource for EV batteries. Meanwhile, food and beverage processing, especially halal-certified products, is expanding to meet rising domestic and regional demand, creating fertile ground for long-term investment in Indonesia.
2. Renewable Energy
The government is taking decisive steps to reduce fossil fuel dependence and expand renewable energy capacity. With the world’s second-largest geothermal reserves, Indonesia is a hotspot for solar, wind, and geothermal projects. Investors benefit from tax holidays, import duty exemptions, and majority ownership allowances. Public-private partnerships are actively driving large-scale solar farms and wind initiatives, making investing in Indonesia’s green energy sector not only profitable but globally impactful.
3. Mining and Natural Resources
Indonesia holds significant deposits of nickel, copper, coal, and gold, resources critical to global supply chains. With a shift toward value-added processing, supported by policies that restrict raw material exports, the mining sector offers stability and future-proof potential. The basic metal industry is expanding to meet demand from EV and construction markets, further reinforcing investment in Indonesia’s resource-rich landscape.
4. Tourism and Hospitality
Driven by population growth and nationwide health coverage programs, Indonesia’s healthcare sector is evolving rapidly. Opportunities abound in hospital infrastructure, pharmaceutical manufacturing, medical devices, and telemedicine. Multinational and local firms are increasing production capacity, making this a high-impact sector for investment in Indonesia, especially with its growing middle class and aging population.
5. Agriculture and Agribusiness
Agriculture remains vital to the Indonesian economy. The country is a leading producer of palm oil, rubber, coffee, and cocoa. With a growing focus on sustainable practices, the palm oil sector remains a strong export engine. Meanwhile, fisheries and aquaculture are expanding through innovative and sustainable methods.
How Does Indonesia’s Strategic Location Benefit Global Investment?
Located at the crossroads of major international shipping lanes, Indonesia connects Asia, the Middle East, and Europe. Government-backed infrastructure upgrades, including seaports, airports, toll roads, and special economic zones, support seamless regional and global trade. As the largest economy in ASEAN, Indonesia offers investors access to a combined market of over 600 million people, making it a strategic launching pad for companies expanding across Southeast Asia.
What Are the Main Challenges of Investment in Indonesia and How Can They Be Overcome?
Investment in Indonesia presents immense potential, but investors must navigate several structural challenges to unlock its full value. Investors often face shifting regulations, overlapping jurisdictions, and time-consuming licensing processes. However, many investors find success by working with reputable local partners who understand the landscape and by selecting industrial zones where licensing and infrastructure are already streamlined.
Currency volatility and commodity dependence can affect returns, yet these risks are manageable through portfolio diversification, long-term planning, and investing in export-oriented sectors that offer natural hedges. Also, infrastructure bottlenecks and logistics inefficiencies add cost and time, but the government’s National Strategic Projects and public-private partnerships are actively improving transport, energy, and connectivity, especially in ready-to-invest zones.
Despite the hurdles, investment in Indonesia remains promising. Choosing locations with ready infrastructure, securing trustworthy local alliances, and leveraging policy support are all critical to navigating the landscape
Why Is Now the Right Time to Consider Investment in Indonesia?
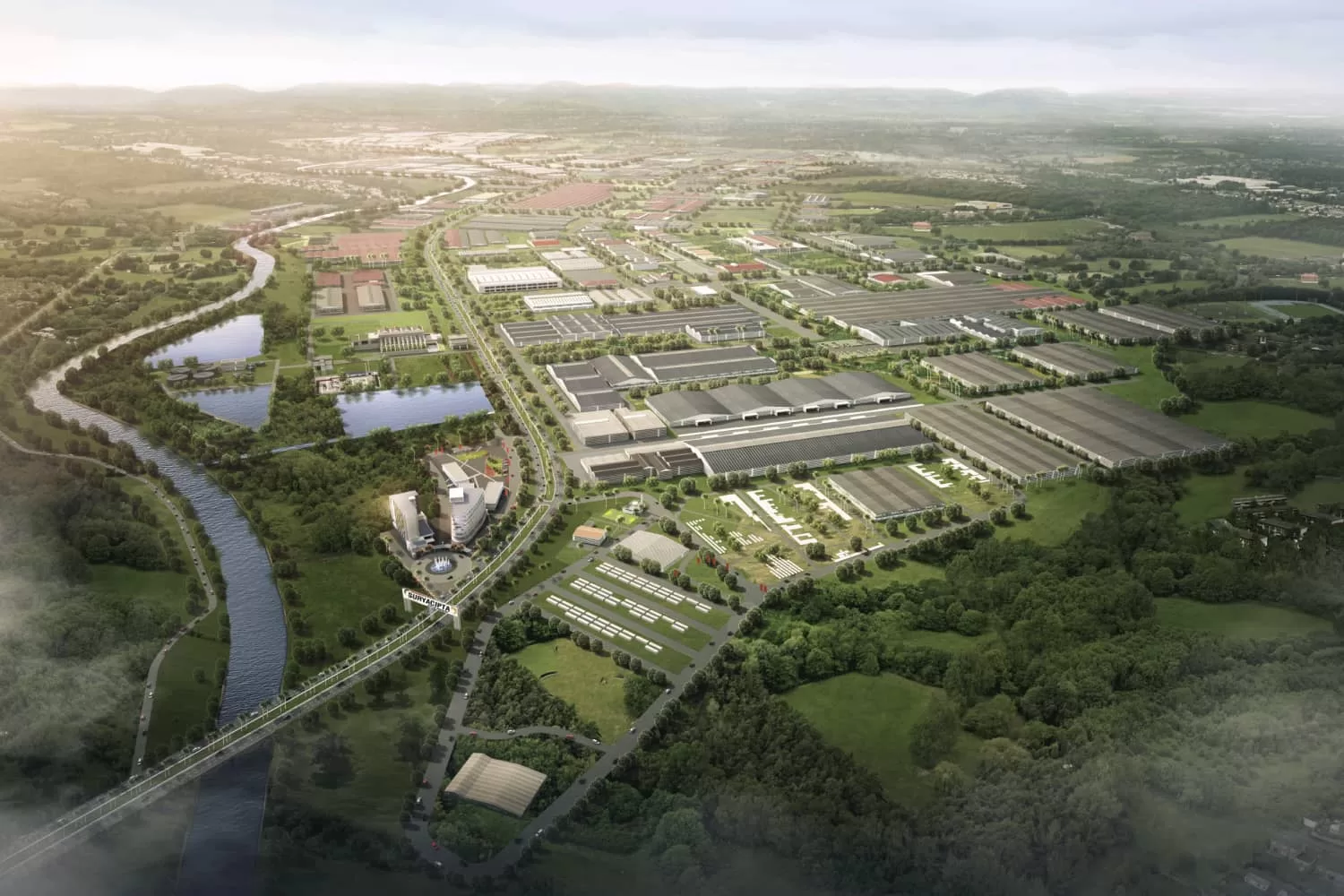

Despite global uncertainties, Indonesia continues to show strong fundamentals of long-term promising potential. Strategically positioned at the heart of Asia-Pacific trade routes, Indonesia offers unmatched regional access.
New economic hubs are taking shape to meet this momentum, and emerging hubs like Subang Smartpolitan in West Java are becoming key investment destinations. With smart infrastructure, sustainability at the forefront, and easy access to major cities, Subang Smartpolitan offers a natural environment for businesses looking to grow in a dynamic and supportive ecosystem.
This is where innovation meets long-term growth to create fertile ground for transformative developments. With the right foundation in place, now is the time to act. If you are interested in knowing more about Subang Smartpolitan, please visit our website to contact us.
FAQ
- How does Indonesia support sustainable investment?
The Indonesian government prioritizes sustainability, offering incentives for renewable energy projects, sustainable agriculture, and eco-friendly development.
- How does Indonesia support foreign investors?
The Indonesian government offers various incentives, including tax holidays, reduced import duties, and special economic zones (SEZs) with streamlined regulatory processes.
- Can foreign investors own land in Indonesia?
Foreign investors cannot directly own land in Indonesia, but they can secure long-term lease agreements or invest through local partnerships or joint ventures.
- What types of businesses are most suitable in Subang Smartpolitan?
Subang Smartpolitan is ideal for manufacturing, logistics, automotive, pharmaceuticals, and high-value industries that require sustainable infrastructure, strategic location, and seamless connectivity to ports and transportation hubs.
- Where is Subang Smartpolitan located?
Subang Smartpolitan is located in Subang, West Java, Indonesia, strategically positioned near the Trans-Java Toll Road, Patimban Seaport (40 km), and Kertajati International Airport (70 km), making it a prime industrial hub.